As hundreds of millions of metric tons annually of plastic debris and waste are discarded after use they do not just "go away." Discarded manmade plastics of all sorts gradually degrade from sunlight, temperature variations, salt water and mechanical impacts. Microplastics are tiny particles and fibers of human manufactored plastic products such as nylon and polyethylene. They are 5 millimeters or less in length. View microscopic images of microplastic fibers HERE . You may be shocked! |
Just because you can't see
something does not validate the opinion that it is not a problem.
Microplastic fibers, fragments
and debris... what are they and why do
we need to know about these worldwide micro pollutants?
Read on...
we need to know about these worldwide micro pollutants?
Read on...
Worldwide plastic production creates over 350 million metric tons of added stress on the environment annually; and only a small percentage of the plastic is recycled. The multiple of diverse products that utilize
 plastics
in manufacturing has
resulted in a problem not suspected to arise even just a few years
ago. Today, environmentalists are making us aware that the
diacarded, unused or broken plastic breakdown products are rapidly
accumulating in overburdened landfills, dumps, and huge mounds on
unconstrained bare land deposits... and uncountable tons end up in
fresh water, oceans at every depth, and even in rainwater.
plastics
in manufacturing has
resulted in a problem not suspected to arise even just a few years
ago. Today, environmentalists are making us aware that the
diacarded, unused or broken plastic breakdown products are rapidly
accumulating in overburdened landfills, dumps, and huge mounds on
unconstrained bare land deposits... and uncountable tons end up in
fresh water, oceans at every depth, and even in rainwater. And
yes, they are found in humans worldwide!
BACKGROUND:
FROM: OURWORLDDATA.org In the marine environment: In 2018, the production of plastics totaled around 359 million metric tons worldwide. It is estimated that plastic lines, ropes and fishing nets comprise 52 percent of the plastic mass in the ‘Great Pacific Garbage Patch’ (GPGP) (and comprises 46 percent of the megaplastics component of the GPGP). Most river plastic originates from Asia, which represents 86 percent of the global total. This is followed by Africa at 7.8 percent, and South America at 4.8 percent.
It’s
estimated that there are
more than 5 trillion plastic particles in the world’s surface waters.
DEGRADATION OF PLASTICS IN THE ENVIRONMENT:
Microplastic objects are any plastic particle 5 millimeters in diameter or less which is about the size of a poppy seed. The discarded plastics on land surfaces such as dumps, landfills, along roadways eventually end up "over there". Temperature
 ,
sunlight, microorganisms, dissolved chemicals, and abrasion break down
the plastic waste into ever smaller fragments and fibers.
Unfortunately microplastics in waterways attract toxins to their
surfaces and so carry the toxins along with the plastic to the water's
bottom and are often consumed by minute developing larvae of insects
and fish!
,
sunlight, microorganisms, dissolved chemicals, and abrasion break down
the plastic waste into ever smaller fragments and fibers.
Unfortunately microplastics in waterways attract toxins to their
surfaces and so carry the toxins along with the plastic to the water's
bottom and are often consumed by minute developing larvae of insects
and fish!Recognition that polymeric (repeating natural or manmade chemical groups linked together forming clumps or strands) macromolecules make up many important natural substances such as the cellulose, eventually man made (synthetic) plastic polymers were created having a variety of properties. Commercial products include thousands of familiar synthetic polymers. Examples of these man made materials are numerous configurations of fibers, flexible films, adhesives, resistant paints and tough, hard products... all of which have contributed to the transformation of our society.
TRY THIS AT HOME: Pay special attention to the throwaway plastic materials you go through in a week. You will be surprised at the amount of waste generated from grocery bags and trash can liners. We've all been frustrated in attempting to pry, cut, twist, chisel, and/or hammer open a hard plastic package enclosing a tool or kitchen utensil. Plastic films degrade quicker than the hard plastic items. Films most commonly used are drop cloths used as barriers in construction, garbage bags, cling-type food wrappers, and bubble wrap. At the end of your week of plastic waste observation and realizing that in the USA alone 128 million other households are doing just what you do with plastic waste, is there any wonder there is a planetary health hazard from discarded macro plastics and subsequent degraded micro plastic particles?. See EarthIsSick.com for a shocking presentation about our planet's current health status.
| Atomic structure of polyethylene |
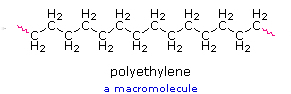 |
 EXAMPLES
OF PLASTIC BASED PRODUCTS:
EXAMPLES
OF PLASTIC BASED PRODUCTS:Plastics are constructed of polymers...repeating moleules stacked tightly together and bound by atomic electrostatic charge onto other identical molecules. There are many different materials made of plastic polymers being utilized for diverse applications. Just a few are listed below:
_________________________________
The eight most common types of synthetic organic polymers, which are commonly found in households are:
Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) White milk bottles all sizes, bleach type bottles, washing machine liquids and some bottle caps.
High-densitypolyethylene HDPE products are commonly recycled. Items made from this plastic and include containers for milk, motor oil, shampoos and conditioners, soap bottles, detergents, and bleaches
Lo2-density Polypropylene (PP) Plastic bags, plastic wrapping, cling film.
Polypropyline Butter and margarine tubs, clear fresh soup containers, some bottle caps
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) Clear bottles (look for a line on the bottom of the bottle), food trays, toys, piping, wire insulation caps
Polystyrene (PS) Yogurt pots, insulated disposable cups, some trays, parcel packaging.
Nylon nylon: multiple products such as combs for your hair, hinges, bags, bearings, clothes and gear wheels.
Teflon (Polytetrafluoroethylene) PTFE industrial coating, fabric and carpet coatings, Cooking surfaces coated with PTFE prevents food from sticking to the pots and pans, nail polish..
Thermoplastic polyurethanes (TPU) Very resistant to heat, instrument panels, caster wheels, power tools, sporting goods, medical devices, drive belts, footwear, inflatable rafts, and a variety of extruded film, sheet and profile applications.
|
|
|
What can we do about
plastic waste defiling the planet's land, air and oceans?
Learn
more at these links below:
|
THE GOOD NEWS ABOUT REMEDIATION
See fibers in food, go HERE